Understanding the Science of Sleep
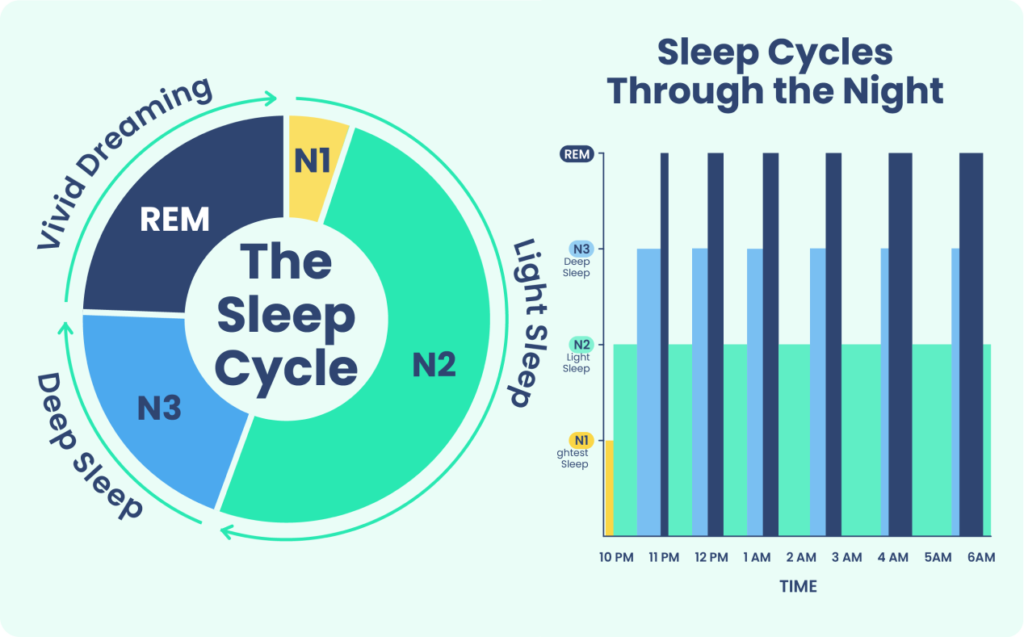
In a normal sleep period, a person experiences 4 to 6 sleep cycles.
- Rapid eye movement (REM) sleep makes up 20% to 25% of total sleep in healthy adults.
- As you cycle through non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep, various bodily functions slow down or stop altogether. Metabolism drops by around 15% Trusted SourceNational Library of Medicine, Biotech InformationThe National Center for Biotechnology Information advances science and health by providing access to biomedical and genomic information.View Source and both heart rate and blood pressure go down.
- Stage 3 NREM sleep or “deep sleep” is believed to be the most critical stage of sleep for regenerating your body and brain. Deep sleep decreases across the lifespan, with one receiving less deep sleep as they age.
- On average, we spend about two hours per night dreaming Trusted SourceNational Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS)NINDS aims to seek fundamental knowledge about the brain and nervous system and to use that knowledge to reduce the burden of neurological disease.View Source , mostly during REM sleep.
- On average, adults sleep on their side 54% of the time Trusted SourceNational Library of Medicine, Biotech InformationThe National Center for Biotechnology Information advances science and health by providing access to biomedical and genomic information.View Source , on their back 38% of the time, and on their stomach 7%.
- While cycles vary in length, each sleep cycle can last about 90 minutes.
SleepFoundation.org (2023)
